Nelle telecomunicazioni, dato un determinato canale, si utilizza il termine throughput per riferirsi alla capacità di trasmissione effettivamente utilizzata. Il termine throughput non è perciò sovrapponibile con la “capacità del link” perché questo secondo parametro esprime la frequenza trasmissiva massima alla quale i dati possono essere scambiati attraverso il canale di comunicazione.
Windows 10 integra una impostazione che di fatto potrebbe limitare il throughput impegnando il canale di comunicazione in misura minore rispetto a quanto sarebbe invece possibile. Il sistema operativo, infatti, utilizza un parametro chiamato Regolazione automatica finestra ricezione che si occupa di definire in maniera autonoma la “taglia” della finestra di ricezione dati.
Di che cosa si tratta?
Sulle reti TCP ogni pacchetto dati inviato da un certo mittente deve necessariamente ricevere un riscontro – detto acknowledgement o ACK – circa la sua avvenuta corretta ricezione (ne abbiamo parlato anche di recente nell’articolo Connessione lenta, colpa del backup di Google Foto e di Windows 10).
Quando il mittente non riceve l’ACK, la trasmissione viene temporaneamente sospesa e, se l’attesa supera un certo limite, si procede con una nuova trasmissione del pacchetto dati.
Il parametro RWIN (TCP Receive Window) indica il quantitativo di dati che possono essere ricevuti prima che debba essere obbligatoriamente inviato un ACK al mittente.
Se, sulla rete, non vi è perdita di pacchetti, la “dimensione” della finestra di ricezione può limitare il throughput.
Il throughput, infatti, si ottiene dalla formula RWIN/RTT dove RTT (round-trip time) è il tempo che impiega il segnale per raggiungere l'”interlocutore” e tornare indietro (è generalmente dell’ordine dei millisecondi).
Il valore RTT determina quindi quanti dati possono essere inviati prima dell’ACK. Se un pacchetto dati ha dimensione di 1.000 byte e RTT è pari a 1 secondo, si possono trasferire al massimo solo 1.000 byte in un secondo dal mittente al destinatario.
Se, tuttavia, il mittente fosse situato nella stessa rete LAN – ad esempio nella stanza accanto – RTT sarà pari a 0,001 secondi (1 ms) e di conseguenza si potranno trasferire 1.000 byte ogni millisecondo quindi 1.000.000 byte (1 MB) al secondo.
Per incrementare le velocità di trasferimento dati da server che sono fisicamente posizionati “dall’altra parte del mondo” si fa in modo che possano essere trasferiti contemporaneamente più pacchetti dati prima di ricevere i vari ACK. È questo il parametro RWIN visto in precedenza.
Appare evidente, quindi, di come il valore RWIN ponga un limite superiore sul throughput ottenibile.
Quando l’utente utilizza Windows 10 e, contemporaneamente, è dotato di una connessione a banda ultralarga (i.e. fibra ottica) può capitare che il throughput risulti limitato rispetto all’effettiva capacità del link.
Nel caso in cui si dovessero rilevare strane difformità, è possibile aprire il prompt dei comandi (Windows+X, Prompt dei comandi, amministratore) e digitare quanto segue:
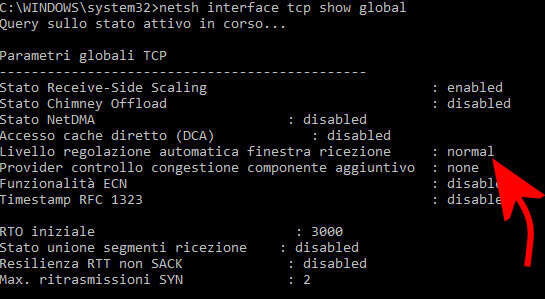
netsh interface tcp show global
Di default, accanto alla voce Livello regolazione automatica finestra ricezione, si leggerà normale. È Windows 10, insomma, per impostazione predefinita, a regolare autonomamente il valore RWIN.
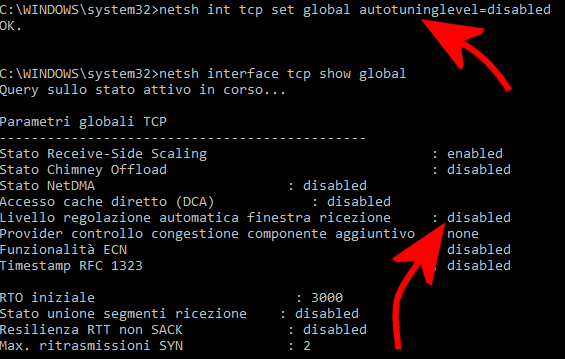
Se il throughput sembrasse limitato con Windows 10 usando connessioni dati a banda ultralarga, un test da effettuare consiste nell’utilizzare il seguente comando in modo da disabilitare l’autoregolazione della “taglia” della finestra di ricezione da parte del sistema operativo:
netsh int tcp set global autotuninglevel=disabled
Il comando netsh int tcp set global autotuninglevel=normal consente, in qualunque momento, di ripristinare la configurazione predefinita.
In alcuni casi Windows 10 utilizza poi l’euristica per adattare la “dimensione” della finestra di ricezione alla tipologia di connessione in uso (se impostata come privata oppure come pubblica: Differenza tra rete pubblica e rete privata in Windows 10).
Per verificare i profili utilizzati, si può impartire il comando netsh interface tcp show heuristics mentre netsh interface tcp set heuristics disabled disattiva solamente l’euristica (impostazione di un valore RWIN “ad hoc” a seconda della specifica tipologia di connessione).
Anche qui, sostituendo enabled nel precedente comando, si può eventualmente riattivare l’euristica.
Autore: IlSoftware.it