
I portavoce di Enel Open Fiber spiegano in che modo la fibra ottica raggiungerà le utenze finali. Previsto anche l’utilizzo di una soluzione fixed wireless per le zone più critiche (case sparse).
Enel Open Fiber, società direttamente controllata da Enel, ha chiarito in che modo intende raggiungere i clienti finali con la sua connettività in fibra ottica.
L’azienda, che com’è noto, si è aggiudicata l’intero primo lotto (primo bando Infratel Italia) e che è in pole position anche nell’ambito della seconda gara, utilizzando le sovvenzioni statali realizzerà le infrastrutture di rete per portare la banda ultralarga nei cluster C e D (le cosiddette aree “a fallimento di mercato”): Banda ultralarga nelle aree a fallimento di mercato: TIM non presenterà alcuna offerta.
L’azienda amministrata da Tommaso Pompei ha però in programma anche un’ulteriore attività ossia la copertura in banda ultralarga di molte altre città del Paese ove vi è già concorrenza.
Il “piano nazionale” di Enel Open Fiber prevede attualmente la copertura in fibra ottica di 270 città entro il 2022: tutte saranno raggiunte con servizi di connettività fino a 1 Gbps.
Nelle aree bianche (a “fallimento di mercato”) attingendo ai fondi messi a disposizione da Infratel e MISE, invece, si arriverà a 100 o 30 Mbps in downstream.
Fibra Enel, quali le soluzioni tecnologiche utilizzate?
Ma come verrà portata la fibra Enel agli utenti finali?
Innanzi tutto, vale la pena ricordare che Enel Open Fiber non venderà il servizio di connettività direttamente agli utenti finali ma offrirà la possibilità di usare la sua rete agli operatori interessati a fronte del versamento di un canone.
Affari&Finanza ha fatto luce, oggi, sulla soluzione che impiegherà Enel.
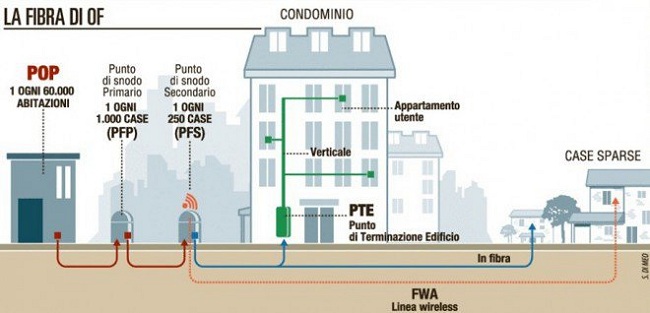
Enel Open Fiber si attrezzerà con un POP, un punto di diramazione ogni 60.000 utenze da servire per poi appoggiarsi a nodi primari (PFP ogni 1.000 immobili) e secondari (SFP ogni 250 immobili).
In corrispondenza di ogni edificio sarà realizzato un nodo di terminazione – probabilmente ove è posizionato l’armadio di distribuzione – per poi raggiungere le singole utenze.
Nelle situazioni più complicate, ad esempio nelle aree rurali in cui sono distribuite case sparse, Enel Open Fiber utilizzerà la tecnologia fixed wireless sui 28 GHz (frequenze ottenute nei mesi scorsi a seguito di una gara indetta dal MISE).
Questa soluzione dovrebbe comunque consentire di trasferire dati in downstream da 30 a 100 Mbps.
L’utilizzo della tecnologia wireless dovrebbe essere comunque molto limitato (circa 200.000 unità abitative in tutto) mentre negli altri casi Enel Open Fiber dovrebbe riuscire ad assicurare connettività FTTH (Fiber-to-the-Home) pura.
Complessivamente, il progetto di Enel Open Fiber prevede di portare la fibra a 9,5 milioni di utenze nelle aree “a successo di mercato” e a 10 milioni nelle zone “a fallimento di mercato”.
Maggiori informazioni sull’attuale copertura della fibra Enel sono reperibili nell’articolo Copertura fibra ottica Enel Open Fiber: eccola nel dettaglio.
Cliccando qui (fonte: Infratel Italia) è possibile scaricare un foglio elettronico che contiene l’elenco completo degli armadi stradali che possono erogare connettività in fibra (o che saranno adeguati a stretto giro) nell’ambito del progetto per il superamento del divario digitale nelle aree a fallimento di mercato (verificare il contenuto delle colonne Stato fibra ottica e Prevista attivazione).
Autore: IlSoftware.it

























